Two major Factors controlling the electronegativity of elements
in the periodic table :
1) Size of the element in the periodic table
2)Position of element in periodic table means closeness to noble gases.
Electronegativity trends part 2 video will help you in understanding the variation of electronegativity in periodic table.
You will get answers of all questions listed below:
Why electronegativity decreases down the group?
Why electronegativity increases along the period?
Variation of electronegativity with atomic size in periodic table
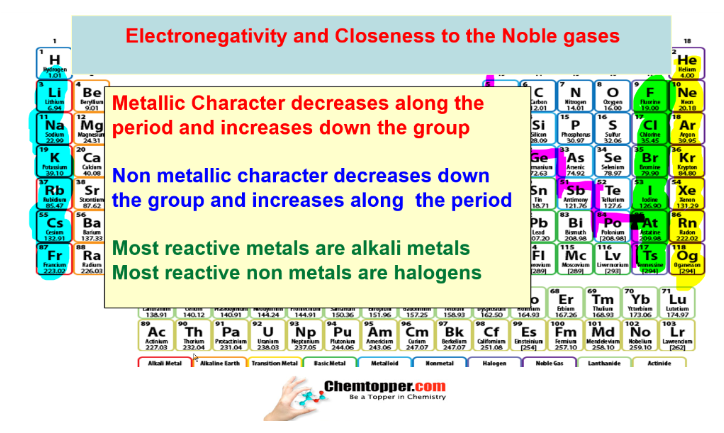
Change in electronegativity as the metallic character increases or decreases
Change in electronegativity as the non metallic character increases or decreases
Why metals are less electronegative than nonmetals?
Why alkali metals are the least electronegative elements of their respective periods in periodic table
Why halogens are the most electronegative elements of their respective periods in periodic table
Which element has the highest value of electronegativity and which element has the lowest value of electronegativity?
And many many more questions you will be able to answer after watching video Trends of Electronegativity in periodic table Part 2
Atomic size and periodic trends in electronegativity
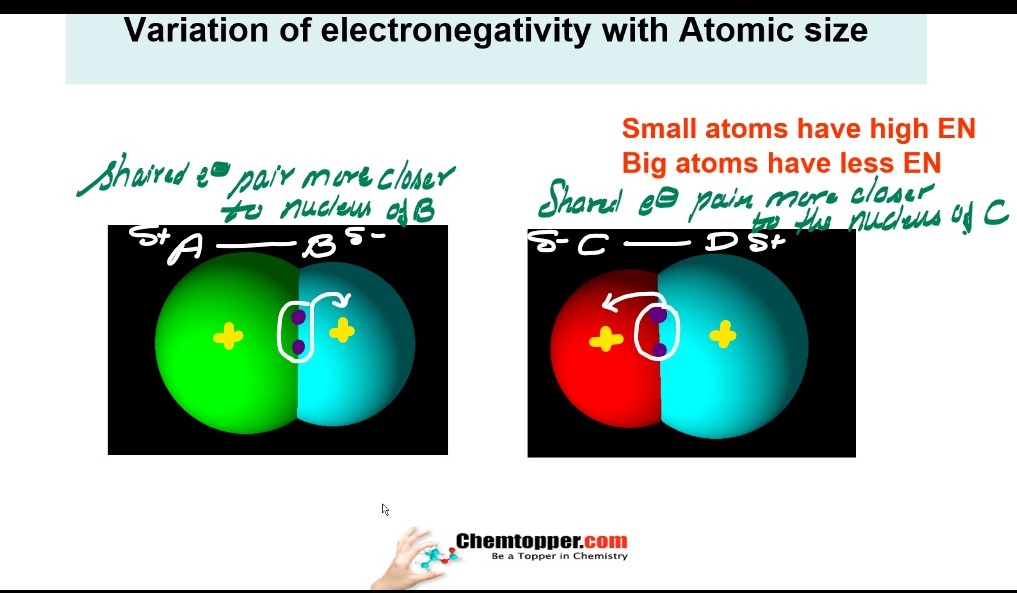
Smaller the atom higher the electronegativity and bigger the atom lesser is electronegativity.
Atomic size down the group increases in the periodic table And along the period atomic size decreases
So it means electronegativity down the group is decreasing and along the period is increasing
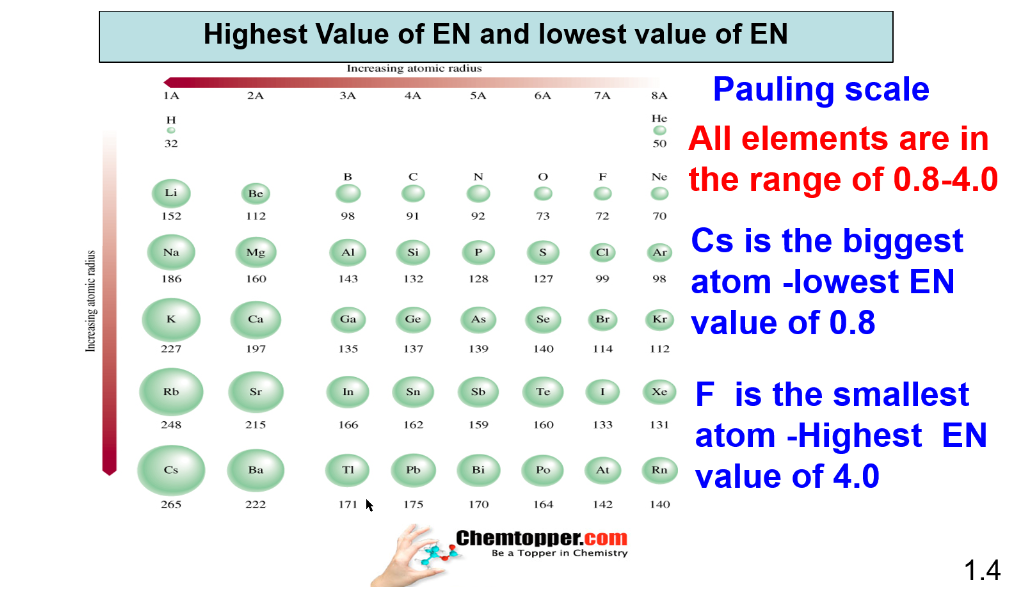
Cesium (Cs) is considered as biggest atom with least value of electronegativity .
Fluorine (F) is considered as smallest atom with highest value of electronegativity.
Metals and non metals :
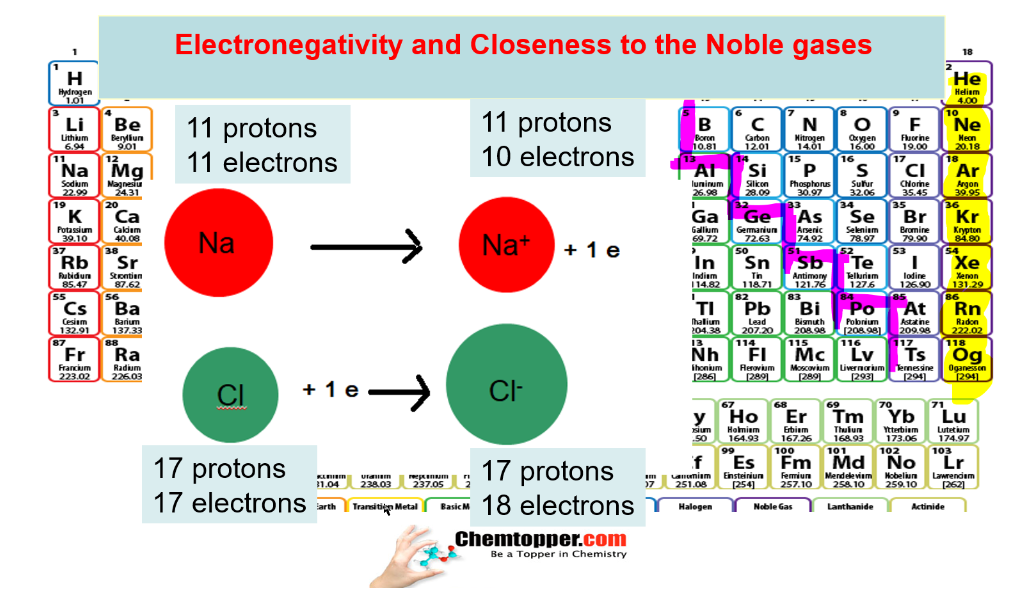
What is the basic difference in metals and nonmetals?
Metals lose electrons to get the nearest noble gas configuration and non metals gain electrons to get the nearest noble gas configuration.
Size and metallic nature of elements in periodic table
Bigger the size of the atom more it has tendency to lose electron because valence electrons are more away from the nucleus and less tightly held.Hence less energy is required to remove electron and atoms become more metallic in nature.
Size and Non -metallic nature of elements in periodic table
Smaller the size of the atom less it has tendency to lose but more tendency to gain electrons because valence electrons are close to the nucleus and more tightly held by the nucleus .Hence it becomes easy to add an electron and atoms become more non metallic in nature.
Variation of metallic character and electronegativity in periodic table down the group and along the period :
Down the group —->atomic size increases —–>
metallic character increases —>Electronegativity decreases
Along the period–> atomic size decreases–>
Metallic character decreases–>Electronegativity increases
Variation of non metallic character and electronegativity in periodic table down the group and along the period :
Down the group —->atomic size increases —–>
Non metallic character decreases —>Electronegativity decreases
Along the period–> atomic size decreases——>
Non metallic character increases—–>Electronegativity increases
Electronegativity and Closeness to the Noble gases
Nonmetals closest to Noble gases are the most electronegative and metals closest to Noble gases are the least electronegative.
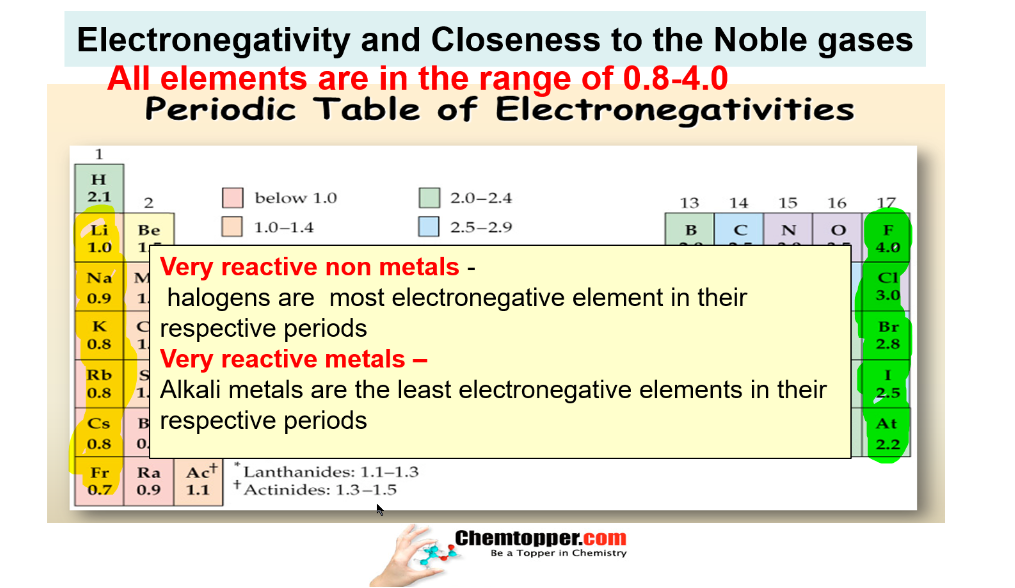
Very reactive nonmetals halogen and very reactive metals alkali metals are
closest to the noble gases.
Halogens are most electronegative in their respective periods as they are smallest in size in their respective periods and closest to noble gases also.
Alkali metals are least electronegative in their respective periods as they are biggest in size in their respective periods and closest to noble gases also.
Watch the video Trends of electronegativity with atomic size and position in the periodic table (EN part 2 ) for understanding the reasoning behind electronegativity trends in the periodic table.
Trends of electronegativity with atomic size and position in the periodic table (EN part 2 )
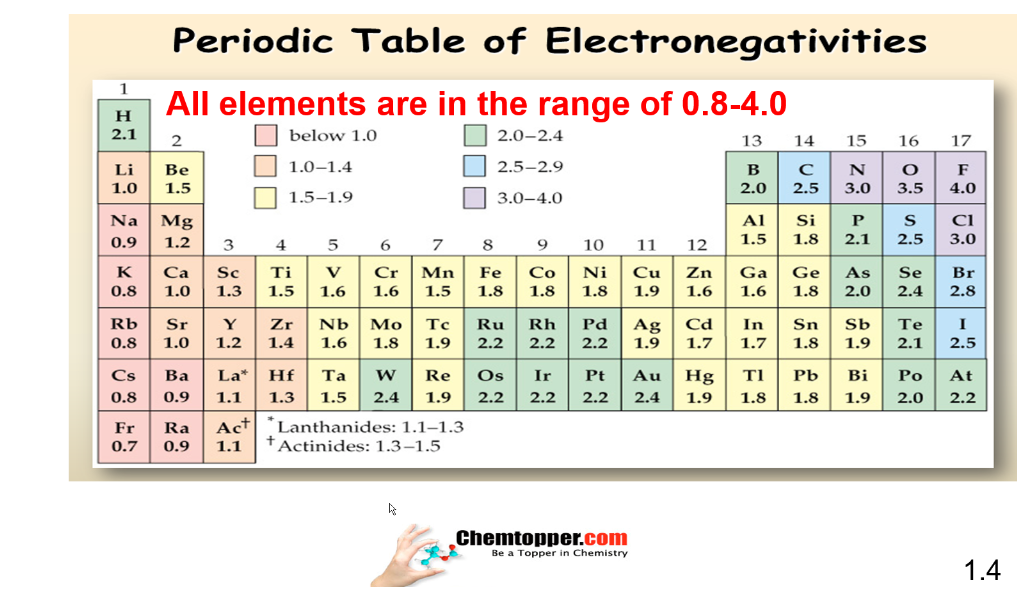
Periodic Chart of electronegativity :
Results
#1. Electronegativity increases with the increase in
#2. Metals close to the noble gases are
#3. Halogens are the most electronegative elements in their respective periods because of the
#4. Alkali metals are the least electronegative elements in their respective periods due to
#5. Pick up the option showing correct charge separation due to difference in electronegativity
#6. Electronegativity decreases with the increase in size because



