Induction and dipole moment:
Induction and bond dipoles represent polarity of a chemical bond.Polarity is due to difference in electronegativity.
Induction and bond dipoles can be explained very well with the help of electronegativity difference.In this video there are plenty of examples discussed to explain the meaning of polarity, induction and dipole.
Examples are discussed to represent Bond dipoles .Like carbon -oxygen chemical bond is a polar covalent bond because electronegativity of carbon is 2.5 and oxygen is 3.0. Oxygen being more electronegative pull electron density of the shared pair of electron on itself and acquires a partial negative charge.However carbon which is bonded with oxygen becomes electron deficient and acquires a partial positive charge.The shifting of electron density in the direction of oxygen due to difference in electronegativity is called as induction. The charge separation due to this difference in electronegativity and formation of partial positive and partial negative is called as Bond dipole.A chemical bond with charge separation due to difference in electronegativity is a polar covalent bond.
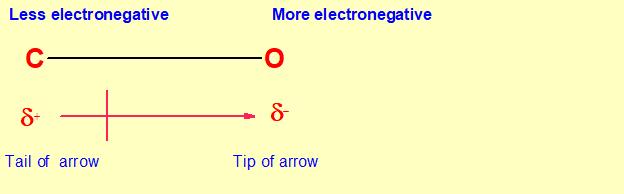
A bond dipole charge separation is represented by an arrow with a tail. The tip of the arrow is in the direction of partial negative charge (electron rich )and the tail of arrow is in direction of partial positive charge(electron deficient).
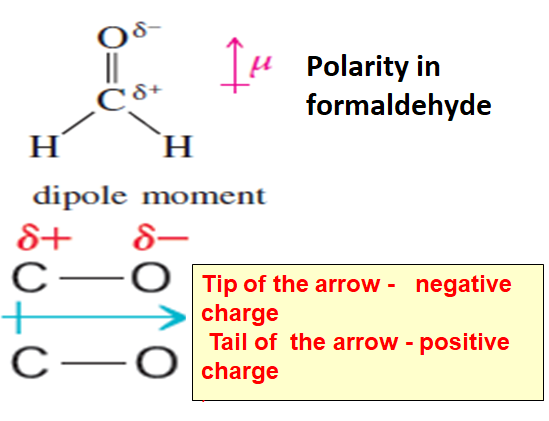
Another example is molecule –formaldehyde
In formaldehyde oxygen is more electronegative than carbon so Carbon -oxygen bond has a polarity.Oxygen has a partial negative charge and carbon has a partial positive charge and bond dipole is represented by an arrow with tip in the direction of negative charge or oxygen atom and a tail and in the direction of positive charge or carbon atom.
Use electronegativities to predict the direction of the dipole moments of the following bonds
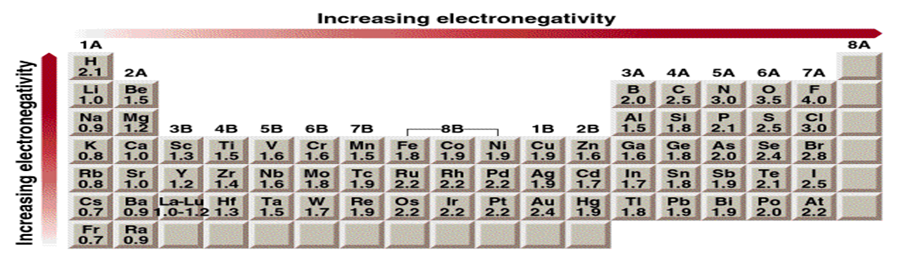
The difference in electronegativity can be used to predict the direction of the Bond dipoles.
Many examples are discussed in videos which can make you expert in identifying a bond dipole.
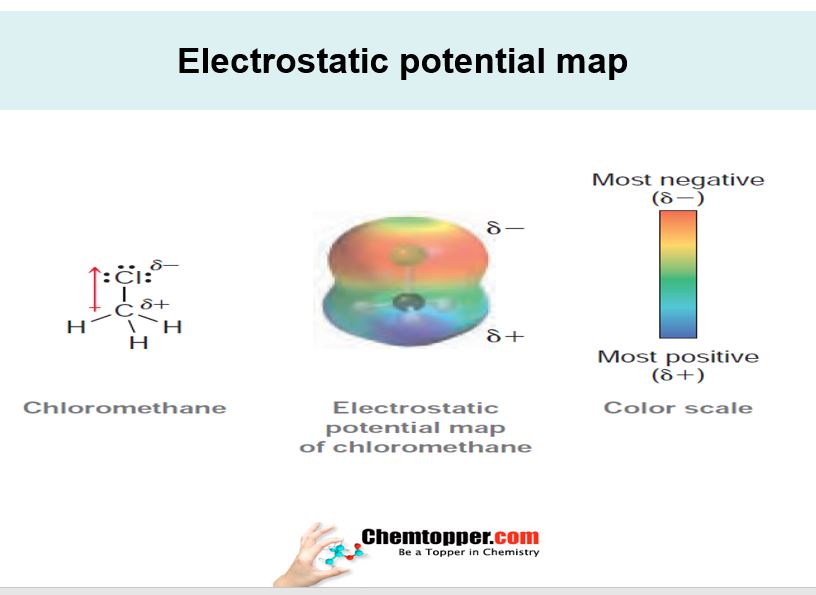
Electrostatic potential map:
Electronic charge distribution in organic molecules are represented by electrostatic potential maps These maps provides symbolic information about electron density and its distribution in the molecule Basically it helps in identifying which part of molecule is electron rich and which part is electron deficient.This helps in predicting bond polarity, dipoles and also the mechanism of the reactions. Negative part is represented by red color and positive part is represented by blue color.
Electronegativity series part 5 – Induction, dipole polarity, and representation of dipoles.
Practice problems Electronegativity series part 5 – Induction, dipole, polarity, and representation of dipoles
Results
#1. Identify in which case the polarity shown is correct:
#2. Identify in which case the curved arrow shown is wrong:
#3. Pick up the correct mechanism of the reaction-
#4. Identify in which case charge separation is not correct :



