Summary Electronegativity part 4 video with a quiz :
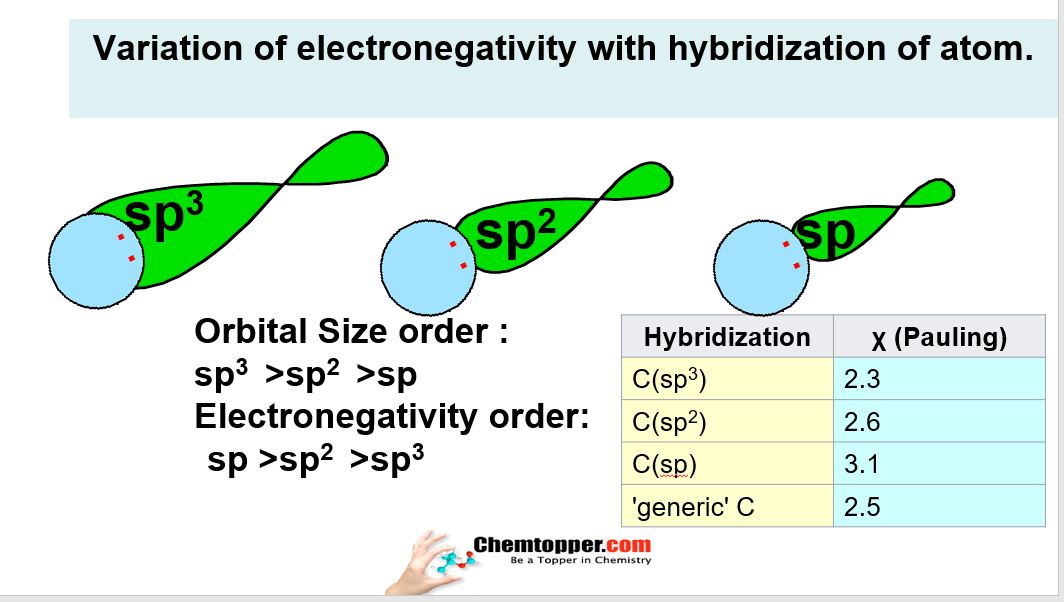
Variation of electronegativity with hybridization of atom:
In Electronegativity part 4 video how electronegativity changes with change in hybridization of the atom.In organic molecules carbon atom can undergo hybridization of SP3 SP2 and SP.You can watch in the video how these hybridized orbitals are formed and how to know hybridization of atoms in organic molecules.
More is the number of orbitals mixed for hybridization more bigger is the size of the hybridized orbital.So it means that SP3 orbitals are more bigger in size then SP2 which are more bigger in size than SP
As we know that electronegativity changes with the change in size of the atoms for the orbitals which are participating in chemical bonding.Big atoms are less electronegativity and small atoms are more electronegative.
So the electronegativity order based on orbital size is SP more electronegative than SP2 which is more electronegative than SP3
we are using this concept in solving the polarity of many carbon -carbon bonds in organic compounds. First identify the hybridization and then compare the electronegativity.
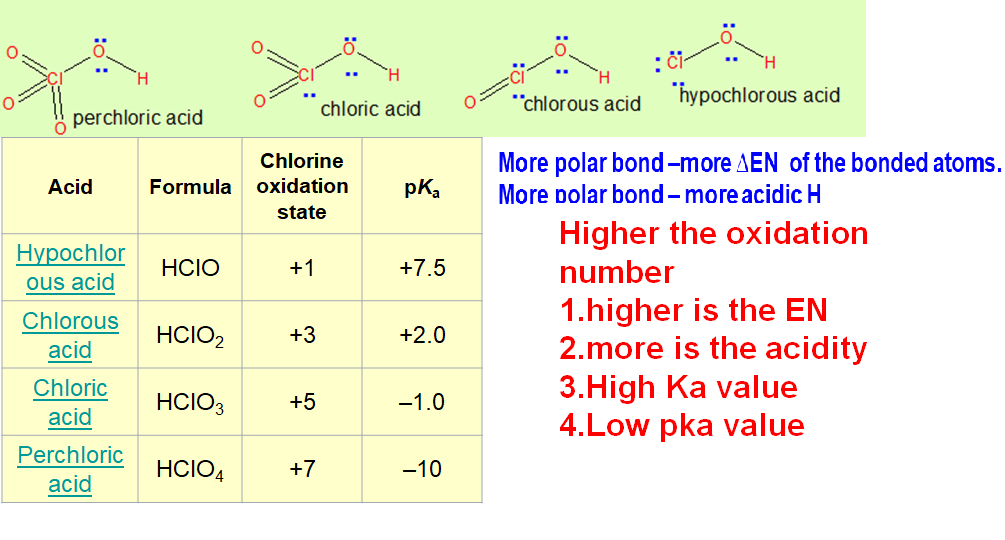
Variation of electronegativity with oxidation number:
In Electronegativity part 4 video how electronegativity changes with change in oxidation number of the central atom and higher the oxidation number more is the electronegativity.
This topic becomes very important to answer many questions based on curved arrow mechanism and acidity of the hydrogen.
Oxoacids of chlorine -Increasing order of oxidation number (more oxygen means higher oxidation number)
perchloric acid > chloric acid > chlorous acid > hypochlorous acid
Here the central atom chlorine has different oxidation numbers- +7 for perchloric acid ,+ 5 chloric acid,+3 for chlorous acid ,+1 hypochlorous acid
Acidity increases as the oxidation number of central atom increases .(watch video for explanation)
Stronger acid has very low pk value and weaker acid has high pKa value.
Remember k a is the acid dissociation constant and strong acid has more dissociation so high value of k a. pka is negative log of ka so high ka value means low pka value
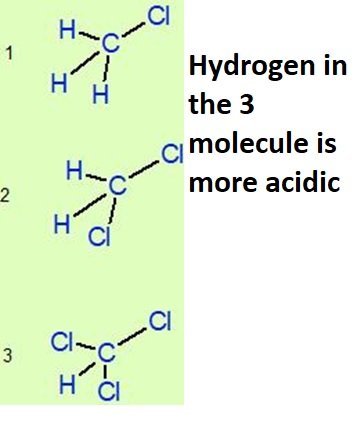
Many questions based on oxidation number,acidity and electronegativities are discussed in the video.
There is question discussed in the video (electronegativity part 4 ) which is clearly showing how acidity of hydrogen’s can be compared in organic compounds.This is one of the most important concept of MCAT and organic chemistry.
One more example is discussed in which number of chlorine atoms are increasing on the central carbon atoms and then comparing oxidation number and acidity of H on the central atom.
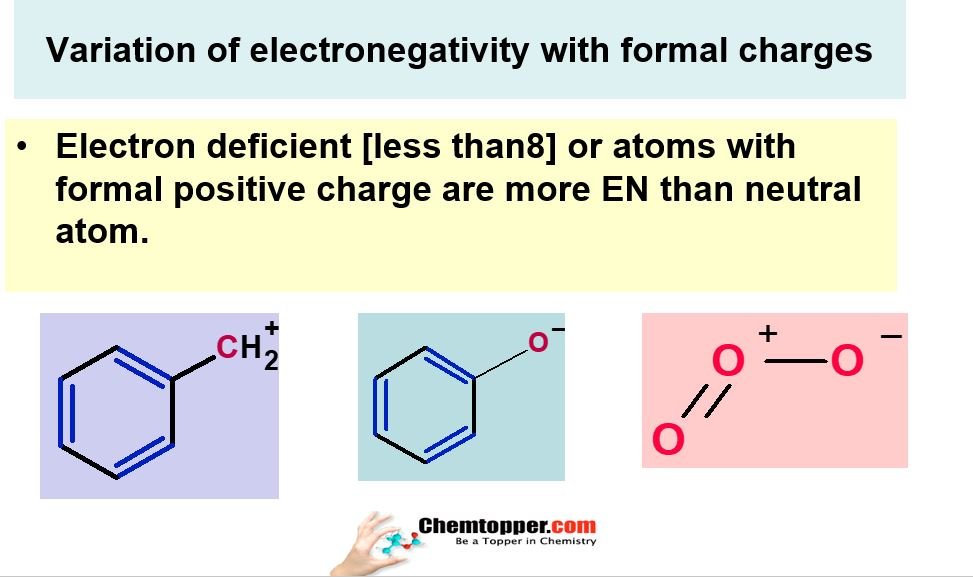
Variation of electronegativity with formal charges:
In Electronegativity part 4 video how electronegativity depends on the formal charges also.If there is an electron deficient atom which has less than 8 electrons or which has a formal positive charge on it.Those atoms are going to be more electronegative than neutral atoms.
Examples of ozone and electron deficient carbocations and electron rich carbanions are discussed with full explanation in the video electronegativity part 4
how to start with the first curved arrow?
In Electronegativity part 4 video how to start with the first curved arrow in resonance is explained.
Resonance is also explained with curved arrow mechanism and how knowledge of electronegativity helps in moving first electron pair in a molecule.(watch video electronegativity part 4 for better understanding of curved arrow mechanisms.
Practice problem on Electronegativity part 4 – Polarity of bonds in organic molecules based on hybridization ,oxidation number and formal charges.
Results
#1. Which carbon is most electronegative ?
#2. Which H is the most acidic hydrogen ?
#3. Identify least acidic proton:
#4. Which carbon is more electronegative -carbon with positive charge (carbocation) or carbon with negative charge (carbanion)
#5. Which structure has the most electronegative oxygen atom?



