Electronegativity part 3 video will help you in understanding how difference in electronegativity controls the nature of chemical bond?
You will get answers of all questions listed below:
How to identify polar Bond based on difference and electronegativity?
How to identify non polar Bond based on difference in electronegativity?
How to identify ionic bond pasting difference in electronegativity?
Which element in the periodic table is the most electronegative element?
Which element in the periodic table is the least electronegative element?
Trends of electronegativity along the period and down the group in periodic table
Why electronegativity not measured in the form of energy?
What is pauling scale?
What is the highest value and the lowest value of electronegativity on the following scale in periodic table?
What is the nature of chemical bond when the difference in electronegativity is less than 0.5?
What is the nature of chemical bond when the difference in electronegativity is more than 1.7?
What is the nature of chemical bond when the difference in electronegativity is in between 0.5 and 1.7?
Different examples of polar ,nonpolar and ionic bonds followed by a quiz which is interactive and will give you a strong foundation in this concept.
And many many more questions you will be able to answer after watching this we video on Electronegativity Part 3 -How to identify Polar Bond, Non Polar Bond and Ionic Bond based on Difference in Electronegativity?
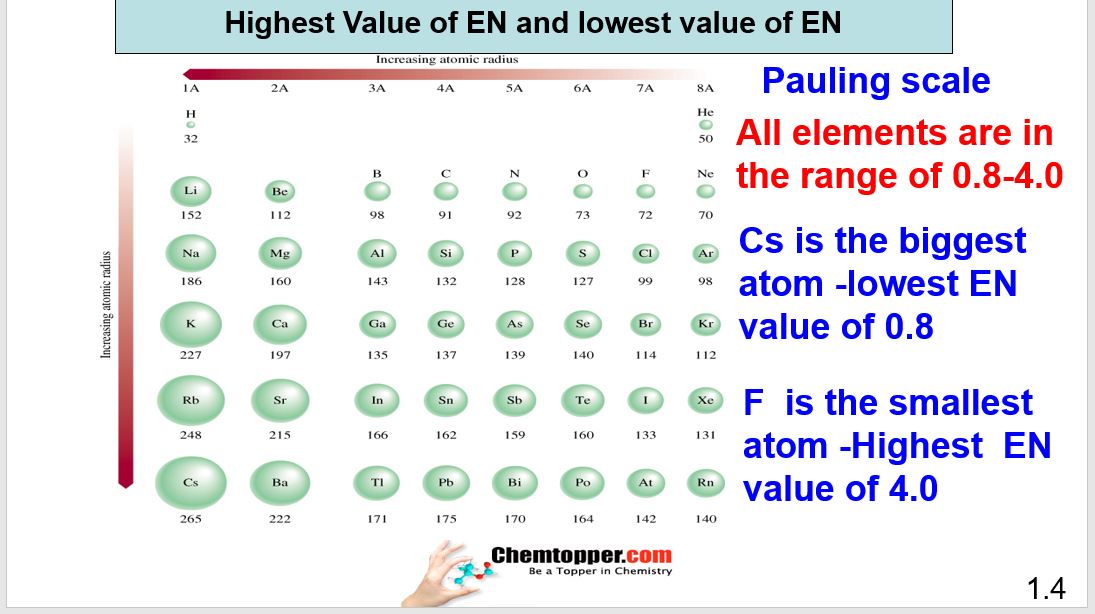
Most Electronegative and Least Electronegative elements in the Periodic table
In the periodic table down the group atomic size increases and along the period atomic size decreases
This means Cesium can be considered as the biggest atom and fluorine is the smallest atom of the periodic table (Noble gases, Hydrogen atom and radioactive materials are generally exempted.)
This means that Cesium has the lowest tendency to attract the shared pair of electrons because of its big size and it is the least electronegative atom in the periodic table. Fluorine is the smallest atom with the highest tendency to attract the shared pair of electron so it is the most electronegative in the periodic table.
Scale to Measure Electronegativity.
Electronegativity cannot be measured in Joules or KJ because it is not an energy. Electronegativity is the tendency to pull shared pair of electrons and hence a different scale is used to measure electronegativity, called as Pauling Scale.
All elements lie in the range of 0.8 (value for Cs -least electronegative) to 4.0(value for Fluorine- most electronegative element)
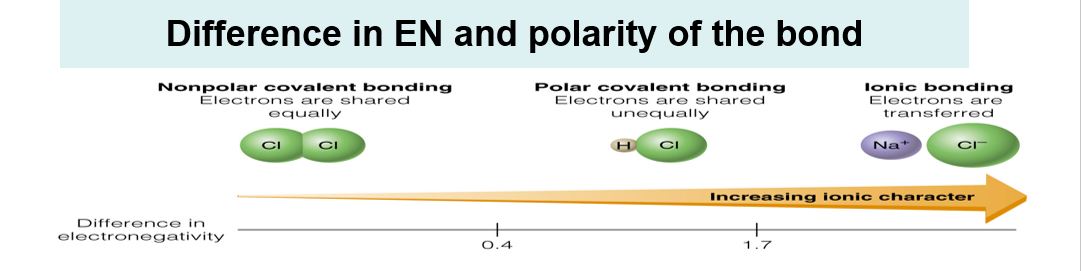
Difference between Electronegativity and Polarity of the Bond
Difference in electronegativity causes polarity of the bond. With higher difference in electronegativity, there is more polarity in a bond. Three basic categories of chemical bonds-
- Polar covalent bonding and
- Ionic bonding
- Nonpolar covalent bonding
When the difference in electronegativity is less than 0.5
For example in Cl2 molecule ,H2 molecule,CH4 and N2 the difference electronegativity is zero because both atoms are identical or in carbon hydrogen bond. In these cases the difference in electronegativity is less than .5 or nearly zero. So bond is Non polar Covalent bond.
When the difference in electronegativity is more than 1.7
When metals are bonded with nonmetals,electrons are not shared but they are nearly transferred. These are Ionic bonds.Example NaCl ,KBr etc.
If the difference lies between. 5 and 1.7
Electrons are shared but not equally between bonded atoms and there is a charge separation.They are polar covalent bonds. As difference in electronegativity increases , polarity of the polar covalent bond also increases.Examples:HCl,HF,H2O etc.
Examples of Polar and Non Polar Bonds:
Non polar bonds: Carbon bonded to carbon or carbon bonded to hydrogen. The difference in electronegativity here is very less or zero.
Polar Covalent bonds: Nitrogen bonded to hydrogen, carbon bonded to oxygen, lithium bonded to carbon.
The polarity increases with the increase in in difference in electronegativity
Ionic bonds generally one is metal other one is non metal and the difference in electronegativity is very large i.e. more than 1.7.
You can now watch this video and practice questions given in the quiz. A better understanding of electronegativity and polarity of bonds will give you a good base for starting Organic Chemistry.
Based on Difference in EN -How to identify polar bond ,non polar bond and ionic bond?(EN-part 3)
Periodic chart of electronegativity

Practice problems on How to identify Polar Bond, Non Polar Bond and Ionic Bond based on Difference in Electronegativity
Results
#1. Which element is the most electronegative element?
#2. Identify the ionic Bond?
#3. Based on the difference in electronegativity identify the most polar Bond
#4. Most electronegative element of the periodic table is
#5. Element with Highest value of electronegativity on the Pauling scale is
#6. Element with lowest value of electronegativity on the Pauling scale is



