By Mehr Grewal
Calorimetry is the science of measuring heat. There are a few important terms you should know about heat. The first one is specific heat capacity, which is a distinguishing characteristic of different substances. Different substances respond differently to being heated, and the specific heat capacity, defined by the amount of energy needed to raise one gram of a substance by 1 degree Celsius or Kelvin. It is usually represented by the letter C, in the following way.
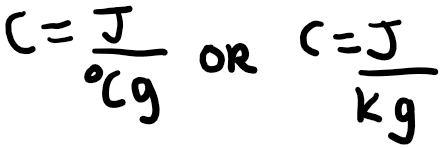
J is the energy in Joules and g represents 1 gram of the substance. The greater the specific heat capacity of a substance, the more energy required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of the substance by 1 degree Celsius or 1 Kelvin. If you would like to write this in terms of 1 mole of the substance, this would be called the molar heat capacity. The symbol for molar heat capacity is usually C n. You can write this with the units below:

Note that you can use either degrees Celsius or Kelvin for heat capacity, as an increase of 1 degree Celsius is equivalent to an increase of 1 degree Kelvin. This is because:
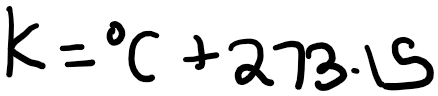
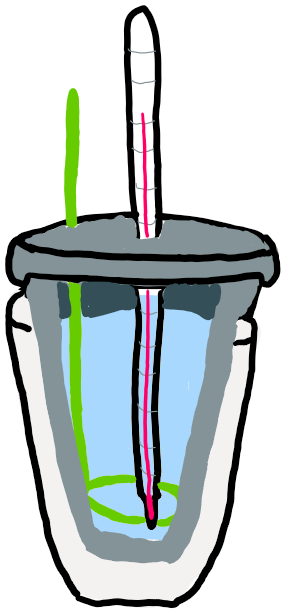
The most simple type of calorimeter is not very precise but can be used for demonstration. This is called a cup calorimeter. It uses 2 Styrofoam cups, one, filled with water and nested inside the other, a stirrer, and a thermometer. It is used to determine the change in energy (heat) that occurs in a reaction, or delta H.
You should know these formulas that we use to calculate energy absorbed and released.
By the law of conservation of energy, also the 1st law of thermodynamics, in a calorimeter, the energy as heat released by the reaction should be equal to the energy as heat absorbed by the solution, assuming no heat escapes. The formula is E= mc x delta T, where m is the mass, c is the specific heat capacity (not to be confused with the speed of light), and delta T is the change in temperature (Tfinal – Tinitial.)
Another important law you should know is known as the zeroth law of thermodynamics, which states that thermal equilibrium is achieved after a certain period of time when 2 substances at different temperatures come in contact with each other; the hotter substance will transfer energy in the form of heat to the colder substance, and at a certain point known as thermal equilibrium, the 2 substances will be at the same temperature and the amount of heat flowing from each substance to the other is the same.
